spring13-AspectJ
1. AspectJ
1.1. AspectJ介绍
AspectJ官网1
AspectJ文档2
1.1.1. pointcuts
pointcuts指的是程序中的某些链接点(某些时机),例如call(void Point.setX(int))表示:调用类Point的setX(int)方法时
pointcuts可以使用与或非表达式(||,&&,!)连接,比如 call(void Point.setX(int)) || call(void Point.setY(int))
pointcuts可以被定义为变量,如下面代码中的move()
1 | pointcut move(): |
当然pointcuts定义的时候还可以使用通配符,比如call(void Figure.make*(..))代表Figure的以make开头且返回值为void的方法(不关心参数)调用的时候。比如call(public * Figure.* (..))代表Figure的任何方法(不关心方法名,参数,返回值)调用的时候。
cflow是什么?
1.1.2. advice
pointcuts 指出了一些事件发生的时机,当这些事件真正发生的时候,我们需要advice表示该做些什么。advice如下,advice可以使用before代表在pointcuts发生以前做一些事情,如下
1 | before(): move() { |
使用after代表在pointcuts发生以后做一些事情,如下
1 | after(): move(){ |
after还可以加上修饰符returning和throwing,分别表示在正常返回和在异常返回的情况,如下
1 | after() returning: move(){ |
around表示环绕一个方法
1.1.3. aspect
aspect是一个特别的类型,在其中可以定义pointcut和advice,如下
1 | aspect MyAspect{ |
当然aspect兼容java,你也可以定义各种方法,变量
1 | aspect MyAspect{ |
1.2. 在IntelliJ IDEA上安装AspectJ
1.2.1. 下载并安装AspectJ
在官网3下载最新版本的jar包,笔者这里的最新版本是aspectj-1.9.6.jar ,下载以后双击运行进行安装。
 AspectJ安装
AspectJ安装
1.2.2. 安装插件
安装AspectJ插件4即可
1.2.3. 启用AJC编译器
在IDEA的设置中选择AJC编译器,并指定1.2.1中安装的ajctool的位置。
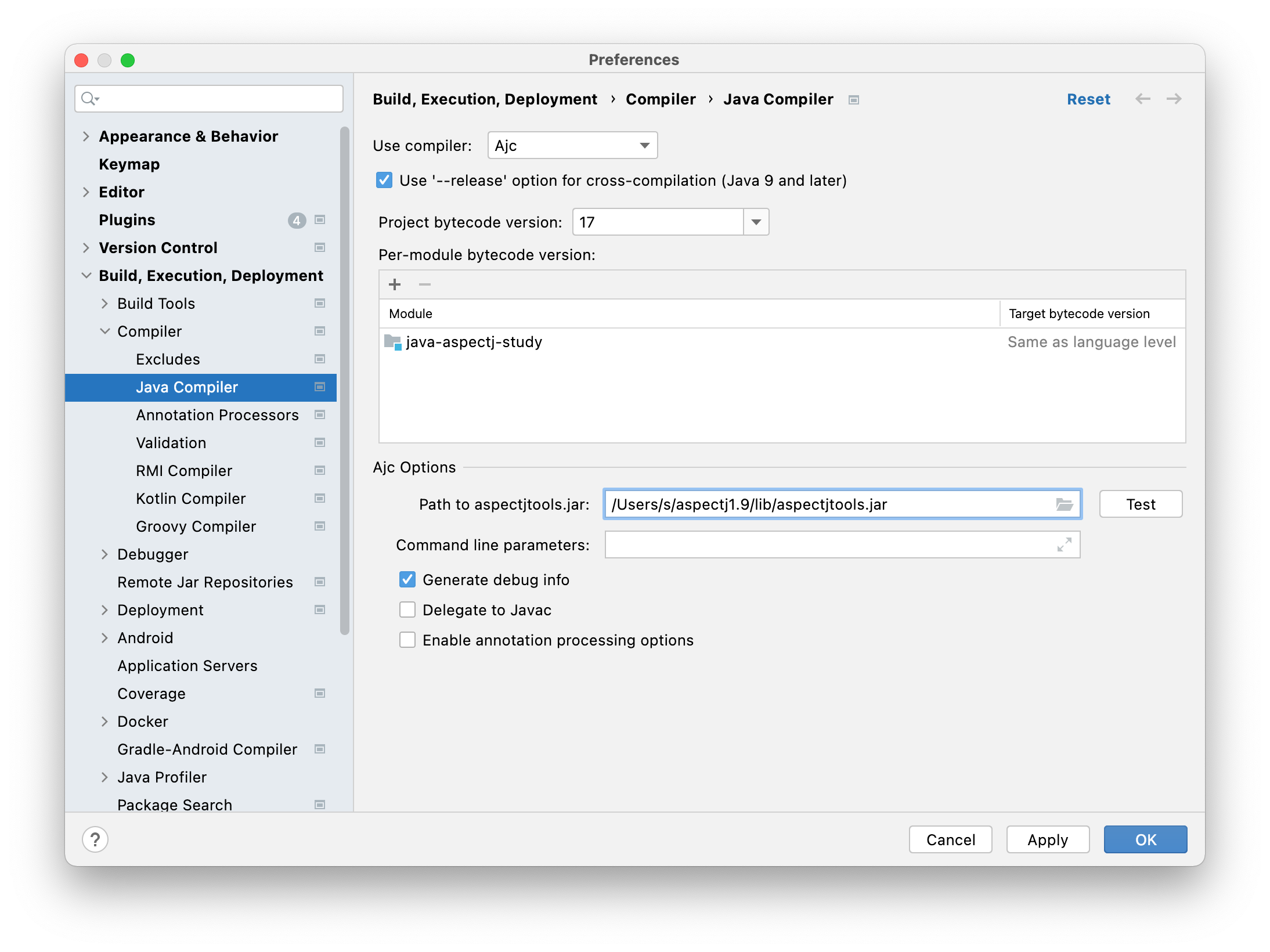 IDEA_Enable_AJC
IDEA_Enable_AJC
1.2.4. 给项目添加AJC依赖
把1.2.1中安装的lib包放到项目的依赖中。
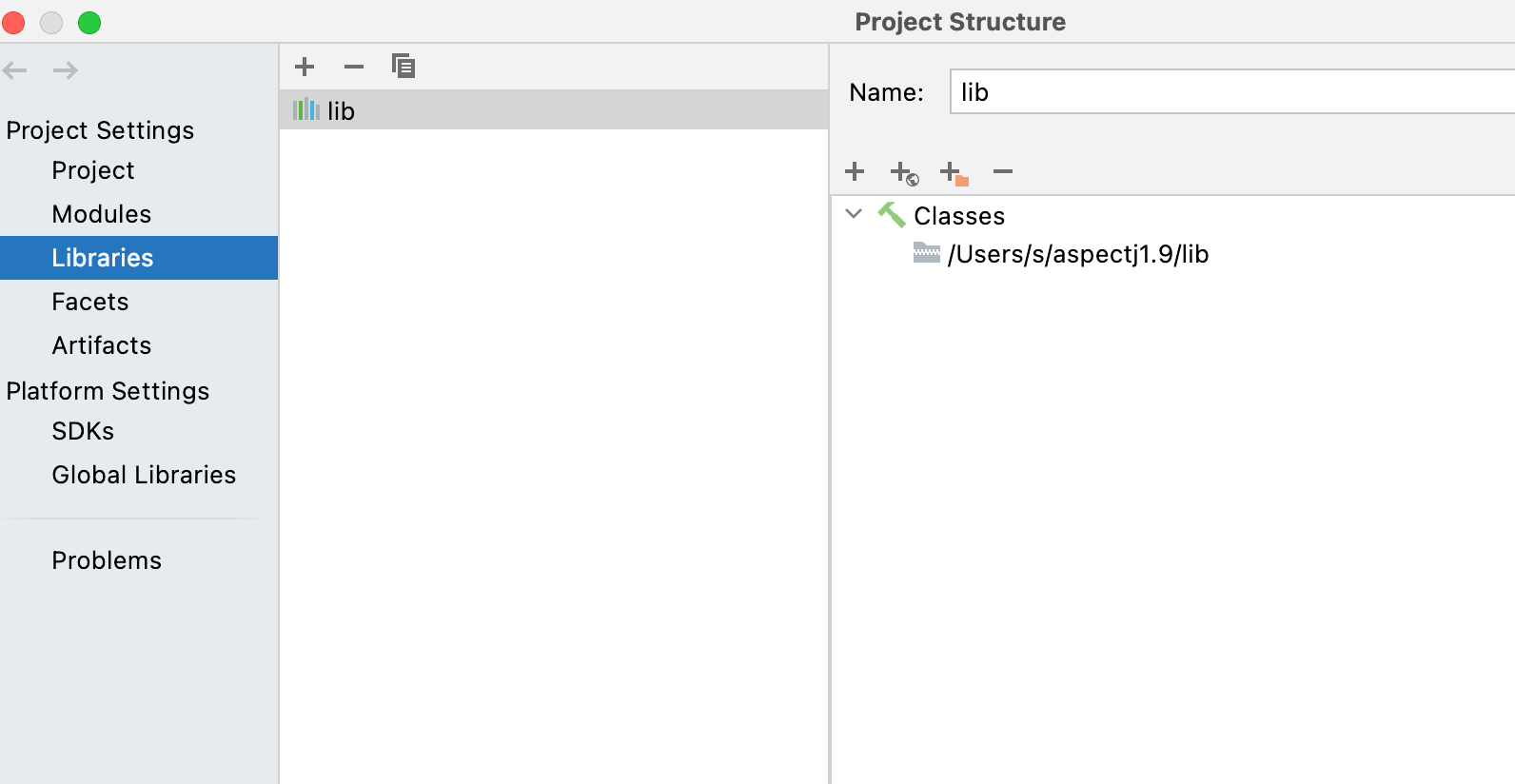 Add_AJC_Lib.png
Add_AJC_Lib.png
1.3. Hello World
下面是一份Helloworld的代码,源程序只输出+号,但是被aspect所拦截,最终输出了Hello + World!
1 | class HelloWorld { |
1.4. Pointcuts表达式
执行一个特定的方法的时候
1
execution(void Point.setX(int))
例如下面的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22class HelloWorld {
public void hello(){
System.out.print("+");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloWorld().hello();
}
}
aspect HelloWorldAspect {
before(): execution(public * HelloWorld.hello(..)){
System.out.print(" Hello ");
}
after(): execution(public * HelloWorld.hello(..)){
System.out.print(" World! ");
}
}被编译为了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
class HelloWorld {
HelloWorld() {
}
public void hello() {
try {
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$before$HelloWorldAspect$1$75869607();
System.out.print("+");
} catch (Throwable var2) {
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$after$HelloWorldAspect$2$75869607();
throw var2;
}
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$after$HelloWorldAspect$2$75869607();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
(new HelloWorld()).hello();
}
}代码被直接写入到了hello方法执行的地方。
调用一个特定方法的时候
1
call(void Point.setX(int))
例如下面的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21class HelloWorld {
public void hello(){
System.out.print("+");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloWorld().hello();
}
}
aspect HelloWorldAspect {
before(): call(public * HelloWorld.*(..)){
System.out.print(" Hello ");
}
after(): call(public * HelloWorld.*(..)){
System.out.print(" World! ");
}
}被编译为了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
class HelloWorld {
HelloWorld() {
}
public void hello() {
System.out.print("+");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorld var10000 = new HelloWorld();
try {
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$before$HelloWorldAspect$1$cdc2ab29();
var10000.hello();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$after$HelloWorldAspect$2$cdc2ab29();
throw var2;
}
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$after$HelloWorldAspect$2$cdc2ab29();
}
}可以看到,是在调用hello方法的前后增加了一些内容。
处理异常的时候
1
handler(ArrayOutOfBoundsException)
如下面的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23class HelloWorld {
public void hello() {
try {
System.out.print("+");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloWorld().hello();
}
}
aspect HelloWorldAspect {
before(): handler(Exception){
System.out.print(" Hello ");
}
}被编译为了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
class HelloWorld {
HelloWorld() {
}
public void hello() {
try {
System.out.print("+");
} catch (Exception var3) {
HelloWorldAspect.aspectOf().ajc$before$HelloWorldAspect$1$ae9a1a78();
System.out.print(var3.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
(new HelloWorld()).hello();
}
}可以发现就是在catch该exception后的第一步操作
当然AspectJ还有很多很多可以定义point cut的关键词,笔者这里就不一一列举了,相见文档5即可
1.5. 总结
所以AspectJ其实是对Java语法的拓展,通过特定的编译器,给Java带来了更强大的能力。
2. Spring 对 AspectJ的支持
官方文档6
Spring支持AspectJ的一个子集,所支持的pointcut如下
Spring AOP supports the following AspectJ pointcut designators (PCD) for use in pointcut expressions:
execution: For matching method execution join points. This is the primary pointcut designator to use when working with Spring AOP.within: Limits matching to join points within certain types (the execution of a method declared within a matching type when using Spring AOP).this: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the bean reference (Spring AOP proxy) is an instance of the given type.target: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the target object (application object being proxied) is an instance of the given type.args: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the arguments are instances of the given types.@target: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the class of the executing object has an annotation of the given type.@args: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the runtime type of the actual arguments passed have annotations of the given types.@within: Limits matching to join points within types that have the given annotation (the execution of methods declared in types with the given annotation when using Spring AOP).@annotation: Limits matching to join points where the subject of the join point (the method being run in Spring AOP) has the given annotation.
spring中的aspectJ,并非使用拓展java语法,而是使用注解来拓展,spring中的aspectj也不是使用的aspectj编译器,而是使用的spring aop来完成代理。但spring也支持通过开关使用原生aspectj7。
aspect的类型用注解@Aspect表示
pointcut字段用@Pointcut表示
advice分别用@Before、@After、@Around来表示